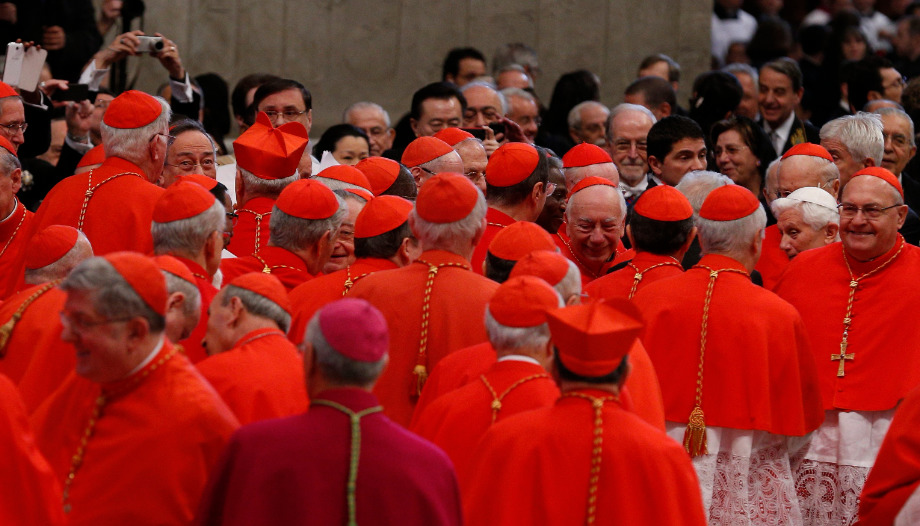
The Holy Father has convoked a consistory. It will be held on August 29 and 30. The day before, he will appoint 21 new cardinals and then they will work on an interesting document: the apostolic constitution of the Holy Father. Predicate Evangelium -on the Roman Curia and its service to the Church-. published last March 19.
Among the new cardinals are three heads of dicasteries of the Curia: the Congregation for Divine Worship, the Congregation for the Clergy, the Pontifical Commission for Vatican City State, and the Pontifical Commission for Vatican City State. Governatorato. Of the new cardinals, 16 are electors, i.e., under 80 years of age, who could be elected Roman Pontiff in a conclave.
What is a cardinal and the College of Cardinals?
The cardinalate is the highest ecclesiastical dignity after the Pope. It is called the "prince" of the Church. Several of the cardinals carry out functions in the dependencies of the Curia - dicasteries - to administer the affairs of the Holy See.
They are appointed by the Pope from among those who meet a series of requirements. As of today, to be named a cardinal, one must have received the order of the presbyterate and be outstanding in doctrine, good morals, piety and prudence. Ordinarily the candidate must be a bishop, but it is possible for the Pope to exempt him from this condition.
All the cardinals make up the College of Cardinals. This body fulfills a dual function, electing the Roman Pontiff and advising him on the government of the Church or any other matter the Pope deems appropriate.
Currently the College of Cardinals is composed of 208 cardinals, of which 117 are electors of a new pope. After the next consistory there will be 229 cardinals, and the total number of electors will be 132.
Who are the members of the consistory and what is their role?
The cardinals, as we said, are part of the hierarchical organization of the Church for its government, and they do so individually or - when they act as a college of cardinals - as a collective. The consistory consists of a formal meeting of the college of cardinals. It represents the highest organ of the supreme and universal government of the Church.
Its origin maintains a close relationship with the history of the Roman presbyterate or body of the clergy of Rome. In the ancient Roman presbyterate there were deacons, in charge of the temporal affairs of the Church in the different regions of Rome; priests, who headed the main churches of the city; and bishops of the dioceses neighboring Rome.
The present cardinals have succeeded the members of the former presbyterate, not only in regard to the offices proper to those three degrees - bishops, presbyters and deacons - but above all by assisting the pope in the administration of the affairs of government of the Church.
What types of consistories are there?
There are three types of consistories: ordinary, extraordinary and semi-public.
The ordinary or secret is so called because no one outside the Pope and the cardinals can be present at its deliberations. It is convened for the consultation of the cardinals present in the Holy City - Rome - on certain grave questions or for the performance of certain acts of the highest solemnity.
The extraordinary meeting is convened when the special needs of the Church or the seriousness of the matters to be discussed so require. It is public in the sense that people outside the College of Cardinals can be invited. This is the case of the appointment of new cardinals, as was the case in August of this year.
And finally the semi-public, so called because in addition to the cardinals, some bishops are part of it, those who reside within a radius of one hundred miles from Rome. In addition, the other bishops of Italy are invited, as well as those who are passing through the Holy City at the time.
What is the rite of creation of a cardinal like?
As for the rite or celebration of the consistory, it usually begins with a brief liturgy of the word, a homily by the Holy Father, and the development of the matter to be discussed. In the case of the consistories of appointment of new cardinals, there is profession of faith and oath, imposition of the cardinal's ring and assignment of the corresponding title, placing of the biretta, and exchange of signs of peace with the Pope and among the new cardinals. On the evening of the celebration, a reception is held to greet the cardinals, and the following day the Roman Pontiff concelebrates Holy Mass with them, in thanksgiving and to pray for their new assignments.
In conclusion to this brief exposition, the faithful should be aware of the imperative need to pray for this instrument of government, since the consistory constitutes the closest collaboration for the Holy Father in the government of the Church.